Michigan Apple Industry Issues
Michigan Apple growers face serious challenges today. With over 850 family-run farms, Michigan ranks as the nation’s second-largest producer of apples in the country. Growers rely on the support of consumers and legislators. Learn about the pressing issues confronting growers and the industry.
H-2A Labor & Michigan Agriculture
Michigan Apple Growers Face Many Challenges Today
Meet the Vargas family, just one of the hundreds of Michigan families working to keep the Michigan Apple industry strong.
Michigan Apple Facts & Growers
The Impact & Challenges of the Michigan Apple Industry
Learn more about the Michigan Apple industry and the challenges apple growers must overcome to continue providing us with locally-grown, fresh fruit. Meet some of the Michigan Apple growers working to make it all possible.
Michigan Apple Industry Issues: Fast Facts
Why the Michigan Apple Industry is a Big Deal
The Michigan Apple industry plays a pivotal role to the state economy, as part of the industry cluster that accounts for over 805k jobs.
A BIG DEAL
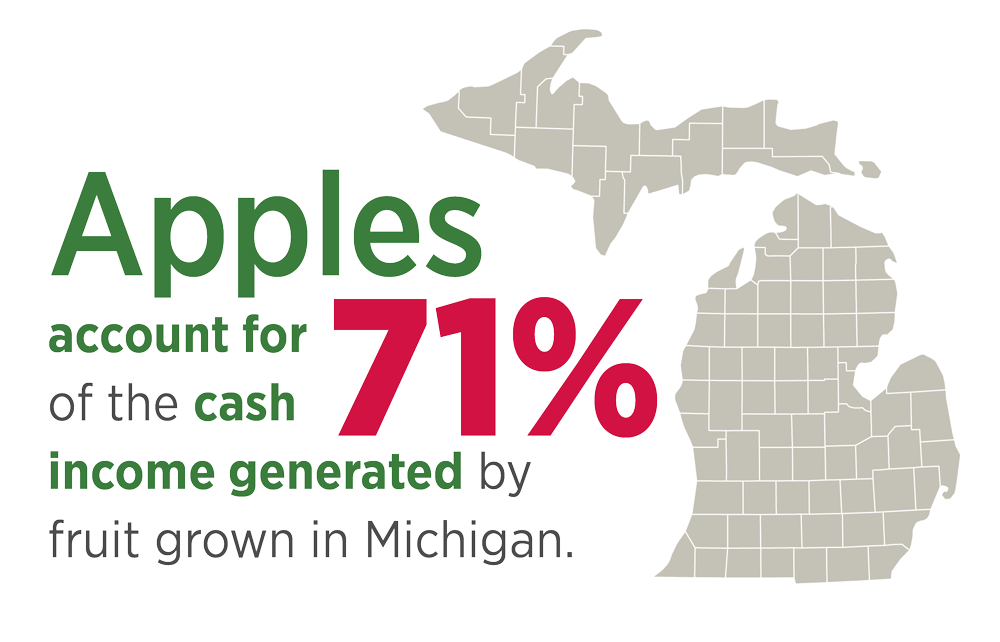
Apples are the largest and most valuable fruit crop in Michigan

Michigan is the second largest producer of apples in the United States. In 2024, Michigan growers harvested an estimated 30.5 million bushels of apples.

Labor Concerns
The oppressive AEWR (Adverse Effect Wage Rate) is an immediate threat to the Michigan Apple industry. In the last decade, the AEWR has increased by 57%, and is 37% higher than Michigan’s minimum wage.

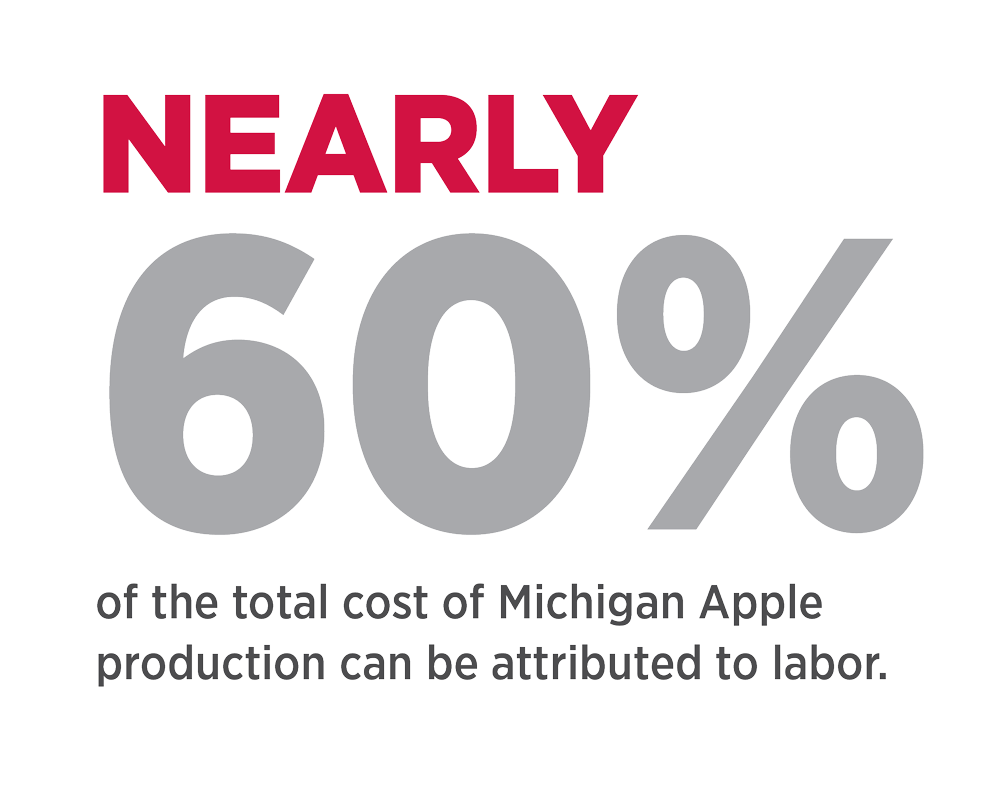
Labor costs are forcing out domestic growers. Nearly 60% of the total cost of Michigan Apple production can be attributed to labor.
The harvest, packing and processing of Michigan Apples requires farm worker hand labor. Michigan has the 7th highest agriculture worker population in the U.S.
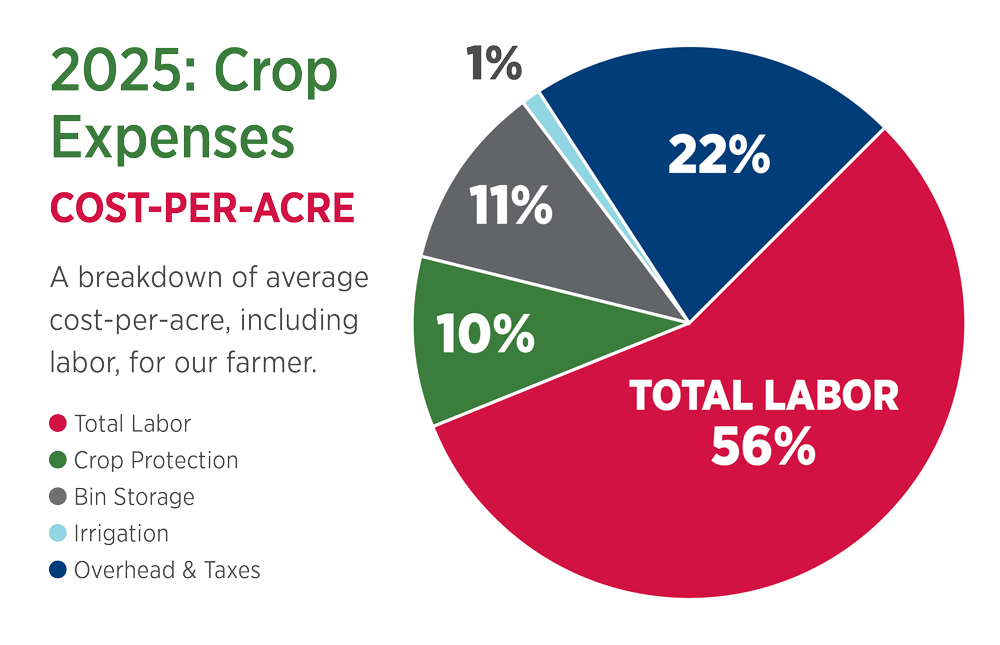
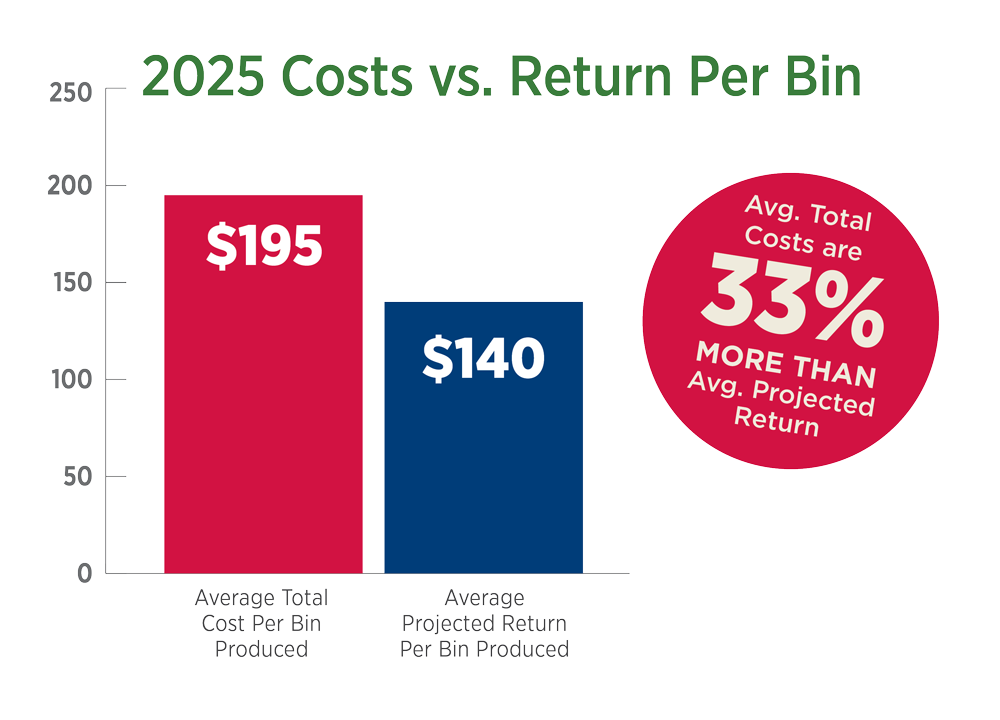
Cost of Production
Average total costs are 33% more than the average projected return. The estimated total projected loss, when applied to a 45 acre farm, is -$135,495.
The Price You See at the Store is NOT What the Grower Earns
If a retailer sells a 3 lb. bag of Michigan Apples for $2.99, the retailer makes $1.06. The grower makes $0.19.
Apple Exports
In 2023, Michigan Apple exports brought a value of $3,137,000 to the industry. Post-pandemic, the Michigan Apple industry recorded a steep increase in apple exports with the 2023-24 crop with bushels shipped increasing by 40%.

Michigan’s food & agribusiness industry employs 17% of the state’s total manufacturing employment, making it the 2nd-largest industry in the state.

Grower Issues In The News
Media Coverage About Michigan Apple Industry Struggles
Consumers and retailers continue to stay engaged in the conversation about the well-being of the Michigan Apple industry, which impacts all of Michigan. Here are just some of the news stories covering Michigan Apple growers and the industry’s issues.
Good Fruit Grower
Cost of Production
Good Fruit Grower
Apple Exports & Tariffs
Fruit Growers News
Declining Consumption
Changing Climate
Find Out More About Apple Grower Concerns
Where to Learn More About Growers’ Challenges
Numerous agricultural and related organizations are working to educate the public about the current concerns of Michigan’s growers. Find out more about the topics highlighted below.
Labor Costs
Soaring Labor Costs
Skyrocketing wage rates due to the H-2A program’s Adverse Effect Wage Rate (AEWR) are threatening the Michigan Apple industry. AEWR has increased a whopping 61% in the last ten years. This increase is unsustainable for growers. Many fourth and fifth-generation apple farms are going out of business as a result of labor costs.
The FWMA
FWMA
In 2023, the Farm Workforce Modernization Act (FWMA) was reintroduced in the United States (U.S.) House of Representatives after failing to pass through the Senate in 2022. If passed, the Act would make a number of reforms to the existing H-2A agricultural visa program, which allows agricultural employers to hire foreign workers on a temporary basis when there is a shortage of farm labor.
Labor Needs
Migrant Labor Needs
Apple production – growing, harvesting, packing – is highly labor intensive. The apple industry is heavily dependent on migrant labor, H-2A and H-2B workers to grow, harvest, pack and process apples. There is no longer an adequate domestic workforce. Growers who rely on domestic workers face labor shortages. A stable, legal workforce is critical.











